자료구조 - 이진 트리(Binary Tree)
1. 트리
- 노드와 링크로 구성된 자료구조
- 계층적 구조를 나타낼 때 사용
- 특징
- 하나의 노드에서 다른 노드로 이동하는 경로는 유일
- 노드가 N개인 트리의 edge의 수는 N-1개
- 그래프의 일종이나 cycle이 존재 X
- 모든 노드는 서로 연결되어 있음
- 하나의 edge를 끊으면 2개의 Sub-Tree로 분리됨 - 구조
- 루트 노드(root node): 부모가 없는 노드, 트리는 하나의 루트 노드만을 가짐
- 단말 노드(leaf node): 자식이 없는 노드(말단 노드, 잎 노드)
- 내부(internal) 노드: 단말 노드가 아닌 노드
- 간선(edge): 노드를 연결하는 선 (link, branch)
- 형제(sibling): 같은 부모를 가지는 노드
- 노드의 크기(size): 자신을 포함한 모든 자손 노드의 개수
- 노드의 깊이(depth): 루트에서 어떤 노드에 도달하기 위해 거쳐야 하는 간선의 수
- 노드의 레벨(level): 트리의 특정 깊이를 가지는 노드의 집합
- 노드의 차수(degree): 하위 트리 개수 / 간선 수 (degree) = 각 노드가 지닌 가지의 수
- 트리의 차수(degree of tree): 트리의 최대 차수
- 트리의 높이(height): 루트 노드에서 가장 깊숙히 있는 노드의 깊이
2. 이진 트리 (Binary Tree)
- 각 노드는 최대 2개의 자식을 가질 수 있음
- 자식 노드는 좌우를 구분함(왼쪽 자식 : 부모 노드의 왼쪽아래, 오른쪽 자식 : 부모 노드의 오른쪽 아래)
- 종류
- 포화 이진 트리 ( Perfect Binary Tree) : 모든 레벨에서 노드들이 모두 채워져 있는 트리
- 완전 이진 트리 ( Complete Binary Tree) : 마지막 레벨을 제외하고 노드들이 모두 채워져 있는 트리
- 정 이진 트리 (Full Binary Tree) : 모든 노드가 0개또는 2개의 자식 노드를 갖는 트리
- 편향 이진 트리( Skewed Binary Tree) - 사향트리 : 한쪽으로 기울어진 트리
- 균형 이진 트리 : 모든 노드의 좌우 서브 트리 높이가 1 이상 차이나지 않는 트리 - 특징
- 포화 이진 트리의 높이가 h일 때, 노드 수는 2^(h+1) - 1 개
- 포화(or 완전) 이진 트리의 노드 수가 N개일 때, 높이는 log2N
- 이진 트리의 노드가 N개 일때 최대 가능 높이는 N-1
3. 이진 트리의 순회
- 모든 노드를 빠뜨리거나 중복하지 않고 방문하는 연산
- 전위 순회(Preorder Traversal)
- 방문 순서 : 현재 노드 -> 왼쪽 노드 -> 오른쪽 노드
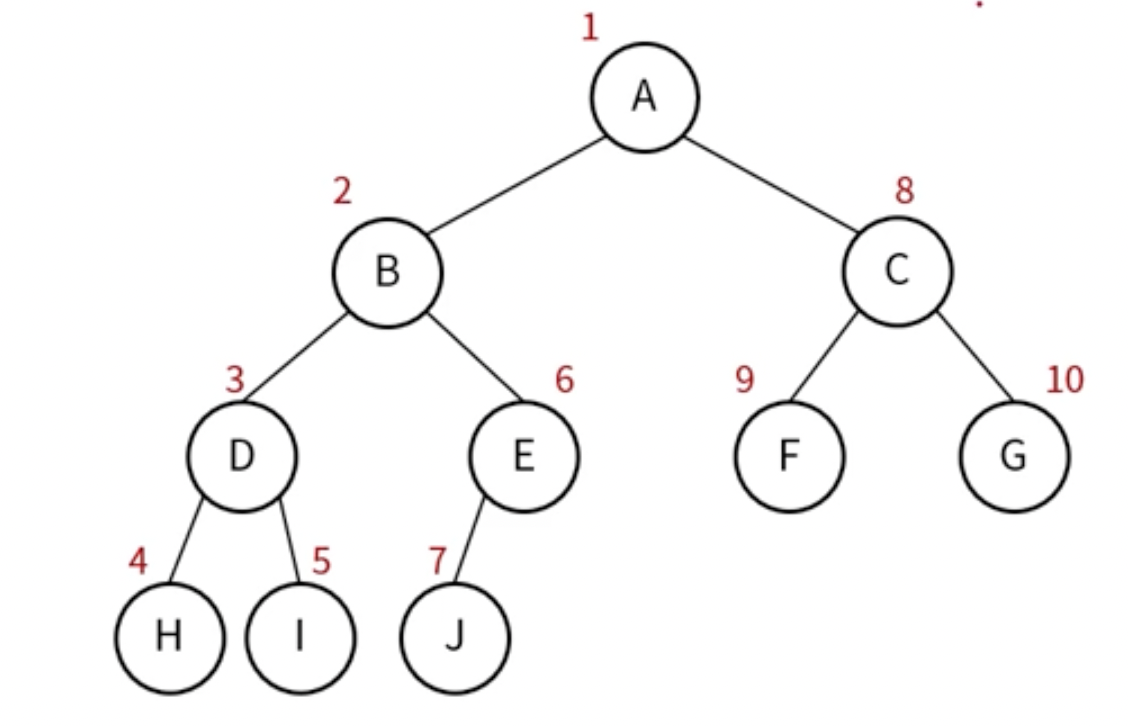
- 중위 순회(Inorder Traversal)
- 방문 순서 : 왼쪽 노드 -> 현재 노드 -> 오른쪽 노드
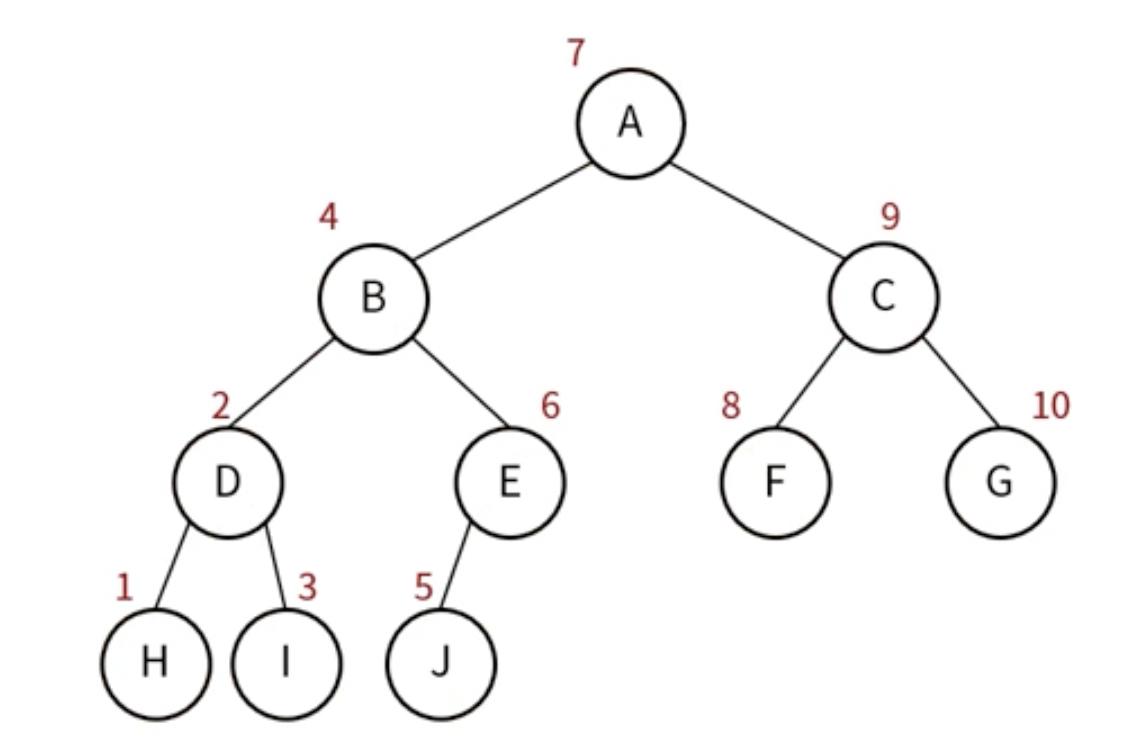
- 후위 순회(Postorder Traversal)
- 방문 순서 : 왼쪽 노드 -> 오른쪽 노드 -> 현재 노드
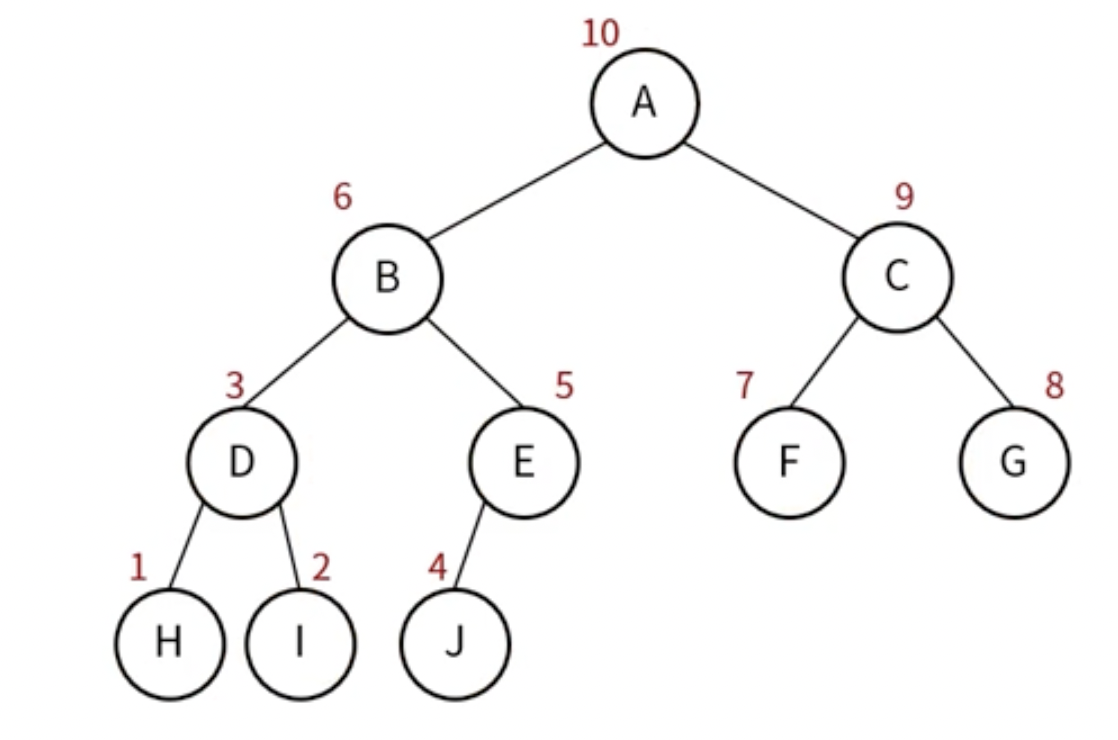
- 레벨 순회(Levelorder Traversal)
- 방문 순서 : 위쪽 레벨 부터 아래로 내려오며 (왼쪽 노드 -> 오른쪽 노드)
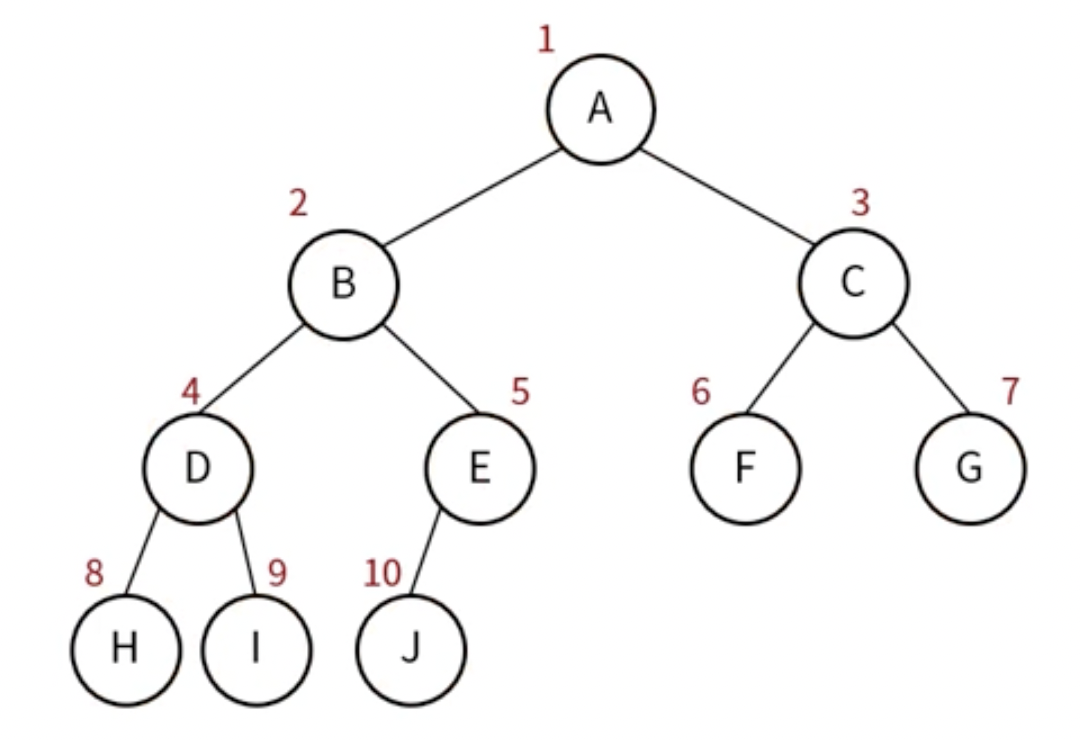
4-1 . 배열로 이진 트리 구현
- 레벨 순회 순으로 배열에 구성

// 배열을 이용한 이진트리 구성, 순회
import java.util.Arrays;
class BinaryTree{
char[] arr;
BinaryTree(char[] arr){
this.arr = arr.clone();
}
public void preOrder(int idx){
System.out.print(this.arr[idx] + " ");
int leftIdx = idx * 2 + 1;
int rightIdx = idx * 2 + 2;
if (leftIdx < this.arr.length){
this.preOrder(leftIdx);
}
if (rightIdx < this.arr.length) {
this.preOrder(rightIdx);
}
}
public void inOrder(int idx){
int left = idx*2 + 1;
int right = idx * 2 + 2;
if (left < this.arr.length){
this.inOrder(left);
}
System.out.print(this.arr[idx] + " ");
if (right < this.arr.length){
this.inOrder(right);
}
}
public void postOrder(int idx){
int left = 2 * idx + 1;
int right = 2 * idx + 2;
if (left < this.arr.length){
this.postOrder(left);
}
if (right < this.arr.length){
this.postOrder(right);
}
System.out.print(this.arr[idx] + " ");
}
public void levelOrder(){
for (char s: this.arr) {
System.out.print(s + " ");
}
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] arr = new char[10];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = (char)('A' + i);
}
BinaryTree bt = new BinaryTree(arr);
System.out.println("== PreOrder ==");
bt.preOrder(0);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("== InOrder ==");
bt.inOrder(0);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("== PostOrder ==");
bt.postOrder(0);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("== LevelOrder ==");
bt.levelOrder();
System.out.println();
}
}
4-2. 연결 리스트로 이진 트리 구현
- 값과 간선을 관리하기 위한 노드로 연결 리스트 구성

import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
class Node{
char data;
Node left;
Node right;
Node(char data, Node left, Node right){
this.data = data;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
class BinaryTree2{
Node head;
Node[] datas;
BinaryTree2(){};
BinaryTree2(char[] arr){
this.datas = new Node[arr.length];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
datas[i] = new Node(arr[i], null, null);
}
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
int left = 2*i + 1;
int right = 2*i + 2;
if (left < arr.length) {
datas[i].left = datas[left];
}
if (right < arr.length) {
datas[i].right = datas[right];
}
}
this.head = datas[0];
}
public void preOrder(Node node){
if (node == null){
return;
}
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
preOrder(node.left);
preOrder(node.right);
}
public void inOrder(Node node){
if (node == null){
return;
}
inOrder(node.left);
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
inOrder(node.right);
}
public void postOrder(Node node){
if (node == null){
return;
}
postOrder(node.left);
postOrder(node.right);
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
}
public void levelOrder(Node node){
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList();
queue.add(node);
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
if(queue.peek().left != null){
queue.add(queue.peek().left);
}
if(queue.peek().right != null){
queue.add(queue.peek().right);
}
System.out.print(queue.poll().data + " ");
}
}
}
public class Practice1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] arr = new char[10];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = (char) ('A' + i);
}
BinaryTree2 bt = new BinaryTree2(arr);
System.out.println("== PreOrder ==");
bt.preOrder(bt.head);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("== InOrder ==");
bt.inOrder(bt.head);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("== PostOrder ==");
bt.postOrder(bt.head);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("== LevelOrder ==");
bt.levelOrder(bt.head);
System.out.println();
}
}
4-3. 트리 구조 복습, 구현
// 트리 구조 복습, 구현
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
class Node2{
char data;
Node2 left;
Node2 right;
Node2 parent;
public Node2(char data, Node2 left, Node2 right, Node2 parent) {
this.data = data;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
this.parent = parent;
}
}
class BinaryTree3{
Node2 head;
BinaryTree3(char[] arr){
Node2[] nodes = new Node2[arr.length];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
nodes[i] = new Node2(arr[i], null, null, null);
}
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
int left = 2*i + 1;
int right = 2*i +2;
if (left< arr.length) {
nodes[i].left = nodes[left];
nodes[left].parent = nodes[i];
}
if (right < arr.length) {
nodes[i].right = nodes[right];
nodes[right].parent = nodes[i];
}
}
this.head = nodes[0];
}
public Node2 searchNode(char n) {
Queue<Node2> queue = new LinkedList<>();
Node2 node = this.head;
queue.add(node);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node2 cur = queue.poll();
if (cur.data == n) {
return cur;
}
if (cur.left != null) {
queue.add(cur.left);
}
if (cur.right != null) {
queue.add(cur.right);
}
}
return null;
}
public void childNodes(char n){
Node2 find = this.searchNode(n);
if (find.left != null) {
System.out.println(n + " left child : " + find.left.data);
}
if (find.right != null) {
System.out.println(n + " right child : " + find.right.data);
}
}
public void parentNodes(char n){
Node2 find = this.searchNode(n);
if (find.parent != null) {
System.out.println(n + " parent : " + find.parent.data);
}
}
public void printLeaf(){
Queue<Node2> queue = new LinkedList<>();
Node2 node = this.head;
queue.add(node);
System.out.print("Leaf : ");
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node2 cur = queue.poll();
if (cur.left == null && cur.right == null){
System.out.print(cur.data + " ");
}
if (cur.left != null) {
queue.add(cur.left);
}
if (cur.right != null) {
queue.add(cur.right);
}
}
System.out.println();
}
public int checkDepth(char data){
int depth = 0;
Node2 cur = this.searchNode(data);
while (cur.parent != null){
depth ++;
cur = cur.parent;
}
return depth;
}
public int checkSize(char data){
Node2 node = this.searchNode(data);
Queue<Node2> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(node);
int size = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node2 cur = queue.poll();
if (cur.left != null) {
queue.add(cur.left);
}
if (cur.right != null) {
queue.add(cur.right);
}
size ++;
}
return size;
}
}
public class Practice2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] arr = new char[10];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = (char) ('A' + i);
}
BinaryTree3 bt = new BinaryTree3(arr);
//Root node
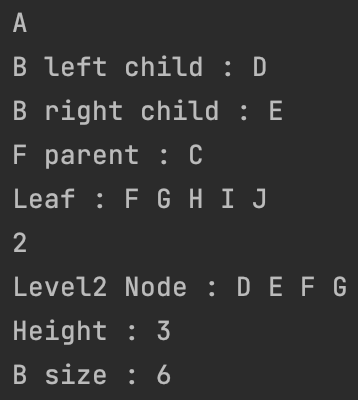
System.out.println(bt.head.data);
//B's child nodes
bt.childNodes('B');
//F's parent node
bt.parentNodes('F');
//Leaf Node
bt.printLeaf();
//E's depth
System.out.println(bt.checkDepth('E'));
//Level 2 Node
System.out.print("Level2 Node : ");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if(bt.checkDepth(arr[i]) == 2){
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
System.out.println();
//Height
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
max = Math.max(bt.checkDepth(arr[i]),max);
}
System.out.println("Height : " + max);
//B's size
System.out.println("B size : " + bt.checkSize('B'));
}
}
5. 연습문제
문제1
- 문제를 이해하는 것과 어떻게 풀어낼지 생각하는데 시간이 많이 걸렸다. 또, 클래스를 만들어 사용하다 보니 바로 솔루션에 구현하기가 어려워 함수를 이용해 풀었다.
/*
종이 접기
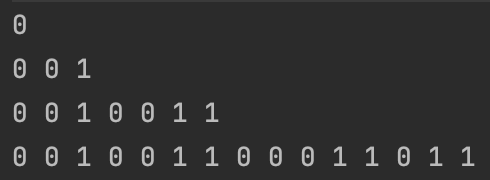
종이를 반으로 접었을 때, 안으로 파인 부분은 0, 볼록 튀어나온 부분은 1이라고 하자.
종이를 접을 때는 오른쪽에서 왼쪽으로 접는다.
종이를 N번 접었을 때의 접힌 상태를 출력하는 문제를 작성하시오.
입력 : 1
출력 : 0
입력 : 2
출력 : 0, 0, 1
입력 : 3
출력 : 0, 0 ,1, 0, 0, 1, 1
*/
class BinaryTreeP{
int size;
int[] arr;
BinaryTreeP(int n){
int size = (int)Math.pow(2,n) - 1;
this.arr = new int[size];
arr[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < size; i+=2) {
arr[i] = 0;
arr[i+1] = 1;
}
}
public void inOrder(int idx){
int left = idx*2 + 1;
int right = idx*2 + 2;
if(left < arr.length){
this.inOrder(left);
}
System.out.print(arr[idx] + " ");
if(right < arr.length){
this.inOrder(right);
}
}
}
public class Practice_p1 {
public static void solution(int n){
BinaryTreeP bt = new BinaryTreeP(n);
bt.inOrder(0);
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
solution(1);
solution(2);
solution(3);
solution(4);
}
}
문제2
- 어떻게 풀어야하는지는 알았지만 코드로 어떻게 구현해야하는지 몰라 막막했던 문제다.
풀이를 보고 다시 풀어보어보았다. 간단해 보이지만 처음부터 이런 재귀함수를 만들기에는 아직 부족하다.

// 각각의 에지에 가중치가 있는 포화 이진트리가 있다.
// 루트에서 각 리프까지의 경로길이를 모두 같게 설정하고,
// 이때, 모든 가중치들의 총합이 최소가 되게 하는 프로그램을 만들어라.
import javax.swing.plaf.metal.MetalTheme;
class BinaryTreeP2{
int h;
int res;
int[] arr;
BinaryTreeP2(int h, int[] w){
this.h = h;
this.arr = new int[(int)Math.pow(2, h+1)];
for (int i = 2; i < this.arr.length; i++) {
this.arr[i] = w[i-2];
}
}
public int dfs(int idx, int h){
if (h == this.h){
res += this.arr[idx];
return this.arr[idx];
}
int left = this.dfs(idx * 2, h+1);
int right = this.dfs(idx*2 + 1, h+1);
res += Math.abs(left - right) + this.arr[idx];
return Math.max(left,right) + this.arr[idx];
}
}
public class Practice_p2 {
public static void solution(int h , int[] w){
BinaryTreeP2 bt = new BinaryTreeP2(h, w);
bt.dfs(1, 0);
System.out.println(bt.res);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int h = 2;
int[] w = {2, 2, 2, 1, 1, 3};
solution(h, w);
System.out.println();
h = 3;
w = new int[]{1,2,1,3,2,4,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1};
solution(h,w);
}
}
'자료구조' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 자료구조 - 균형 이진 탐색 트리(Balanced Binary Search Tree) (1) | 2022.12.30 |
|---|---|
| 자료구조 - 이진 탐색 트리(Binary Search Tree) (0) | 2022.12.30 |
| 자료구조 - 연습문제 (0) | 2022.12.26 |
| 자료 구조 - 해시 연습 문제 (1) | 2022.12.25 |
| 자료구조 - 해시 테이블( 해시 맵, 해시 표) (0) | 2022.12.25 |



